| Brown rot or Bangle blight: Ralstonia solanacearum |
Symptom:
- At the time tuber formation wilt is the main characteristic symptom.
- In leaf symptom -wilt, stunt and yellowing. Browning of xylem tissue.
- Eye buds are black in colour.
- Bacteria ooze coming on infected tuber surface and emits a foul odour.
|
| |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| |
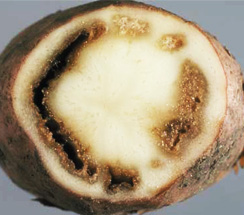
Vascular ring |
|
Oozing out of bacterial exudates |
|
Rotting of vascular tissue |
|
Identification of pathogen:
Mode of spread and survival:
- Infected soil and seed tubers form the main source of the primary infection.
- Brown rot affected plant parts decay and release masses of bacteria in the soil where these may remain viable from season to season.
- The bacteria in the soil are disseminated by wind from one field to the other.
- The infection usually occurs through wounds in the root system.
Epidemiology:
- Temp 25to 35ºC , RH above 50 % and PH 6.2-6.6 favours for the development of disease.
- Acid soil is not favourable.
|
Management:
- Crop rotation of wheat along with potato
- Use resistant varieties like Solanum pujera
|
Source of Images:
http://fera.co.uk/plantClinic/documents/factsheets/brownrot.pdf |

